What is MDM: Official Supports, Features & Aspects
With the ever-increasing digitization in businesses and industries, it's significant to keep security a priority. As many businesses now involve the usage of mobile devices to carry out day-to-day tasks, Mobile Device Management stands crucial.
To highlight this importance, the Zimperium 2023 Global Mobile Threat Report unveils that there had been a 51% increase in the number of unique mobile malware samples year-over-year along with a whopping 80% phishing attacks designed to function on mobiles and desktops. Despite the sensitivity of the data involved, 6 to 10 times users are still more likely to fall for an SMS phishing attack than an email one.
All this brings the importance of MDM to the limelight. MDM gives businesses better control over the mobile devices of their employees leading to not only the enhancement of security but a better incident management approach.
This article explores MDM in detail along with its processes and distinctive elements so you can make the best use of it for your business and streamline your business processes with secure practices.
- Part 1 :What Is Mobile Device Management (MDM)?
- Part 2 :Official Supports for MDM Device Management
- Part 3 :How MDM Works?
- Part 4 :4 Key MDM Features
- Part 5 :BYOD in MDM
- Part 6 :COPE in MDM
- Part 7 :COBO in MDM
- Part 8 :What Is the Key Advantage of Mobile Device Management?
- Part 9 :What Is the Difference between MDM and EMM?
Part 1: What is Mobile Device Management (MDM)?
MDM is an approach to control multiple mobile devices from a single platform. It keeps the connected devices in check in terms of standard security practices. Usually, a MDM tool is used by the IT team of an organization.

According to NIST's Special Publication 1800-21, mobile device management has a significant role in enhancing security, especially for companies that adopt COPE or BYOD policies.
The employees can continue the personal usage of their mobile devices without any hurdles, however, the company IT security practices come into action during the usage and sharing of business data. This way, the business can make the best use of ease provided by the usage of mobile devices, while keeping the security quotient in consideration.
An important point here is that the security practices followed by businesses to secure workstations or desktops stand different than the ones for mobile devices. It's mainly because of the flexibility and multiple dimensions of usage offered by these devices. Therefore, it's important to choose an MDM system that gives the business proper control over the management of connected mobile devices. Also, the MDM must include the business's specific security standards to make it an effective choice for it.
Some of the many threats associated with mobile devices are unauthorized access to sensitive data because of a malicious application, SMS phishing attack, loss of data because of stealing or loss of a device, compromise of confidentiality because of an unauthorized storage platform, and many more.
Therefore, all these points come together to decide the enterprise security architecture. The broader view of mobile device management encompasses the enterprise device management to abide by the standards and policies to help keep the business running.
Part 2: Official Supports for MDM Device Management
This section explores the official supports for Mobile Device Management along with their respective distinctions and features. These official supports include Android Enterprise, Apple Business Manager, and Google Admin.
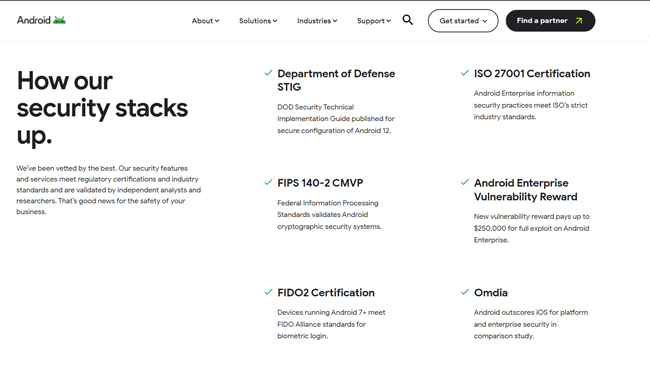
Android Enterprise
Android Enterprise is a comprehensive and secure MDM device management platform that brings together management, innovation, and security solutions in one place.
It supports all sorts of devices from phones to rugged handhelds and kiosks to barcode scanners and smart tablets. Along with that, Android Enterprise is capable of supporting all the devices running on the Android 5.0+ operating system.
With ISO 27001 certification and FIPS 140-2 CMVP, it's safe to say that the Android Enterprise comes with security at its core. Lastly, the platform can be integrated with the Google Play Store and Android Compatibility Program.
Apple Business Manager
Apple Business Manager is a web portal that gives all the required control to the IT administrator over the management of connected devices and allotment of bulk content. The platform supports the iPhone, iPad, and Mac devices. It supports devices running on iOS 7 or later, iPadOS 13.1 or later, macOS 10.9 or later, and tvOS 10.2 or later operating systems.
The Apple Business Manager comes with the ISO/IEC 27001 and 27018 certifications, ensuring the inclusion of security in its architecture. Lastly, it can be integrated with Apple IDs, App Store, Google Workspace, and Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
Google Admin
Google Admin is an extensive and secure platform to help manage your mobile devices. The platform comes with support for Chromebooks and all the other devices running on the Chrome operating system. Also, the Google Admin is capable of getting integrated with the Google Workspace and other productivity tools like Chrome Browser to help have an efficient management and effective control of devices.
Part 3: How MDM Works?
The process of MDM can slightly differ based on the organization's IT infrastructure and security architecture. However, the generic steps remain the same, which are as follows:
1. MDM Software Deployment – To get started with the MDM software, it has to be deployed into the IT admin device. The MDM platform may come as a web portal or a third-party software demanding the installation. Based on its type, cloud or on-premises deployment needs to be carried out.
2. Enroll Devices – Secondly, you need to enroll the devices that need to be controlled. There are several enrollment methods depending on the requirements. These include:
- Device Owner Enrollment: which is a suitable way for fully-owned devices;
- Work Profile Enrollment: for the devices owned by a user but also used for work purposes;
- QR Code Enrollment: which requires the scanning of a QR code to enroll the device;
- Zero Touch Enrollment (best for bulk devices): which requires the assignment of device with the zero-touch portal and it connects the device automatically as soon as its powered on.
3. Configure Devices – Once the devices are enrolled in the deployed MDM system, they need to be configured using the policy file so that all of them are set per the IT policy of the organization.
4. Distribute Mobile Apps and Configure App Settings – With mechanisms like Managed Google Play which allows the users to access a customized Play Store by organization, a business can have better control over the devices.
5. Monitor Device Status – Lastly, it's important to keep monitoring the device statuses for better management and assurance of security practices.
Part 4: 4 Key MDM Features
For any MDM to be a successful choice, it's important to have a few key features. With that being said, the following are four of the key MDM features:
| Manage Mobile Apps | Mobile Applications are an integral part of day-to-day work processes in present times because of their ease of use and flexibility. This makes it important that their security is prioritized for a secure IT infrastructure. MDM software is able to manage and control mobile apps effectively, for example, force installation, configure app settings and update rules, etc. |
| Device Compliance Policies & Kiosk Mode | Security cannot be ensured without having devices that comply with the enterprise's compliance policies. MDM can enforce security policies on work-used mobile devices, such as password rules and network configuration rules. Also, the MDM should have a kiosk mode, which is a feature to make the device restricted running selective applications only. This reduces the pool of possible application installations for the user, ultimately restricting the chances of security breaches. |
| Device Tracking & Monitoring | Since the whole purpose of MDM is to be able to manage and control the devices, without its ability to do that remotely, it fails to serve the purpose. The device tracking can be performed using GPS. With the ability to track the devices, it's easier to locate the devices and find them in case of loss or theft. Moreover, an MDM tool allows the IT admin to track device status and other conditions like data usage, network, etc. |
| Remote Access, Control & Troubleshooting | Most of the device management and control happens remotely. Therefore, the MDM is able to perform remote operations. Some of these operations include the ability to lock the device remotely, erase all the data in case of stealing or loss of the device, being able to perform file transfer, and screen sharing. |
Part 5: BYOD in MDM
Generally, the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) nd MDM are distinctive concepts as one suggests the employees bring their own devices to work whereas the MDM is usually applied on the company-owned devices. However, they both may occur simultaneously where the organization manages and controls the personal devices of the employees for optimized and smooth execution of work.
When it comes to BYOD, there are three main concerns to having a mobile MDM, which include clear policy enforcement, privacy controls, and device compliance checks. What adds to the problem is that all of these need to be executed without affecting the personal usage of employee devices. Under such scenarios, having a separate work mode in the mobile devices is the key factor as it keeps the professional and personal data and applications separate.
Part 6: COPE in MDM
Corporate Owned Personally-Enabled (COPE) is another distinctive enterprise device management concept that contributes to the MDM. The organization usually allots the devices to the employees with the main usage of business, but they can be utilized for personal use as well.
Ensuring successful MDM with the COPE model comes with its own challenges. These include the process of device update, data management, and policy enforcement. If personal or professional usage needs to be compromised, the professional one is kept on priority under this model.
Part 7: COBO in MDM
Corporate Owned, Business-Only (COBO) is the company's device management concept that suggests the allotted device to be used only for business use and prohibited for personal use.
Although the concept ensures security at a high level, it's challenging to keep a check on device usage monitoring and have proper policy enforcement.
Part 8: What is the Key Advantage of Mobile Device Management?
Mobile Device Management allows businesses to ensure digital transformation and abidance by cyber standards, while also keeping security of primary importance. The concept helps streamline the IT infrastructure and security architecture of the organization in an optimal manner. With MDM, the security stays in focus with the assurance of device health maintenance and app update mechanisms.
With effective MDM practices in place, the organization has better control over the employees' devices and data. This helps not only keep the data secure, but the data recovery costs are reduced substantially. Along with that, features like device tracking and remote data erase abilities make it easier for a business to have security in place and keep itself safe from cybercrimes. Lastly, MDM concepts like BYOD help a business save costs while also ensuring the safety and streamlining of data and processes.
Part 9: What is the Difference between MDM and EMM?
MDM is the starting point in the management and control of devices. It gives an organization better control over the employee devices and data for enhanced security and abidance by compliance standards. EMM (Enterprise Mobility Management) takes one step further by covering the management of the entire mobile ecosystem. The EMM also covers the management and control of applications, content, and networks under its umbrella.
EMM covers everything that an MDM does with an additional layer of control over the mobile devices. Some of the common EMM characteristics may include the enforcement of multifactor authentication, application of conditional access, and management of web browser security settings.
All in all, MDM is an essential concept to have a secure IT architecture and ensure compliant digitization processes in an organization. It's important to choose an MDM solution that complies with the business's specific requirements and compliance standards. Lastly, MDM concepts like BYOD, COPE, and COBO can be introduced based on the distinctive business model and processes.
Beginner's Guide to AirDroid Business MDM
If you want more insights into MDM solution features and device compatibility, check here.





Leave a Reply.