[Answered] Are Mobile Hotspots Secure?
Is a personal hotspot secure? To put it simply: They are not.
Hackers can exploit mobile hotspots with different attacks, such as brute force attacks. Through these vulnerabilities, criminals may gain valuable data and even network access.
The best way to protect mobile hotspots is through an MDM like AirDroid Business, enabling IT teams to monitor network activity for high data usage that may indicate excessive hotspot use or even prohibit them altogether.
1 Mobile Hotspot Security Vulnerabilities
The use of a mobile hotspot exposes enterprises to many security vulnerabilities. Attackers will use these attack vectors for many different types of attacks. These are some of the most common ones.
Evil twin attacks
Android-powered devices typically have a default hotspot name, such as AndroidAP. Criminals can use this convention to their advantage by setting up a similar-looking access point, such as AndroidAD, in a high-traffic venue where people are likely to use their hotspot, like a coffee shop.
Some users will mistakenly connect to AndroidAD instead of AndroidAP in their rush. Upon connecting to this "evil twin," criminals may intercept the user's information or inject malicious software via the data traffic.
Brute force attacks
Most users do not elect to change the default password of the mobile hotspot. Some users may create their password but make it too simple, such as one based on their name or a string of repeated characters or numbers.
Attackers can guess these default or weak passwords through what is known as a brute-force attack. As part of this attack, hackers will use sophisticated tools that attempt thousands of possible passwords until the correct one is found.
Upon gaining access to your mobile hotspot, the attacker can monitor and intercept your data or execute lateral execution by compromising other devices on the same network.
Wi-Fi jamming
Like evil twin and brute force attacks, most attacks on mobile hotspots aim to gain unauthorised access, through which the hacker will launch other attacks. Wi-Fi jamming is one of the more unique threats to mobile hotspots: The attacker uses a tool to create interference with the specific frequency it uses.
As a result of the jamming attack, the user will be unable to use Wi-Fi. The attacker can further monitor the success of Wi-Fi jamming by tracking the overall network connectivity or specific events, such as the count of dropped connections. Wi-Fi jamming may thus be used for industrial sabotage, denying employees access to mobile data and their corresponding hotspots.
2 The dangers of mobile hotspot attacks
Although there are many varieties of attacks possible through a mobile hotspot, the consequences can be similar.
Data loss
If attackers gain access to a device, they can steal valuable data. This information can include personal data, such as the employee's login credentials or credit card details, or even company data, such as a database of all its customers.
Sensitive data of this kind can lead to further crime. For example, a hacker could use an employee's login credentials to sign into their email and reset company accounts affiliated with that address. Alternatively, a ransomware group can solicit a cryptocurrency ransom from the company, or it will leak the customer database to the general public.
Operational chaos
Companies benefit more from being proactive rather than reactive when it comes to cyber-attacks. Responding to hacks is much more time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Enterprises have to investigate how the attack occurred, address the vulnerability, and reverse whatever damage the criminals caused, such as resetting affected credentials or clearing devices of malware.
A much more efficient approach is prevention. Companies must actively defend their assets so they do not have to deal with the time sinking of an incident response.

Reputational damage
Ten years ago, people were less concerned about how their data was used. Times have changed in response to a wave of high-profile data breaches. Naturally, consumers and enterprises prefer doing business with organizations prioritizing cybersecurity.
Organizations that suffer from attacks lose credibility here. Customers and clients will be less apt to do business that experience attacks, mainly due to easily preventable reasons such as using insecure mobile hotspots.
3 Regular monitoring to prevent mobile hotspot security vulnerabilities
Regular network monitoring is one way to reduce the risk of attacks through mobile hotspots.
Why network monitoring may be ideal?
Although mobile hotspots present security vulnerabilities, not every company will want to outlaw them altogether. Their employees may have a legitimate use for a hotspot for which there is no other workaround.
For example, an organization with a large sales force may occasionally need business development professionals to connect their laptops to a mobile hotspot to work on a computer.
How to conduct network monitoring?
Network monitoring is best done through an MDM solution, which specializes in managing Android-powered devices.
With an MDM, IT teams can monitor data usage: Employees with unusually high data usage may indicate that they are tethering their laptop to their mobile hotspot so they can perform performance-intensive tasks, such as streaming video or downloading illegal torrents.
In addition to monitoring for excessive usage, IT teams can set up automated triggers. They can elect to receive an alert when an employee exceeds a certain data threshold that may indicate frequent hotspot usage or even a factory reset for egregious cases.
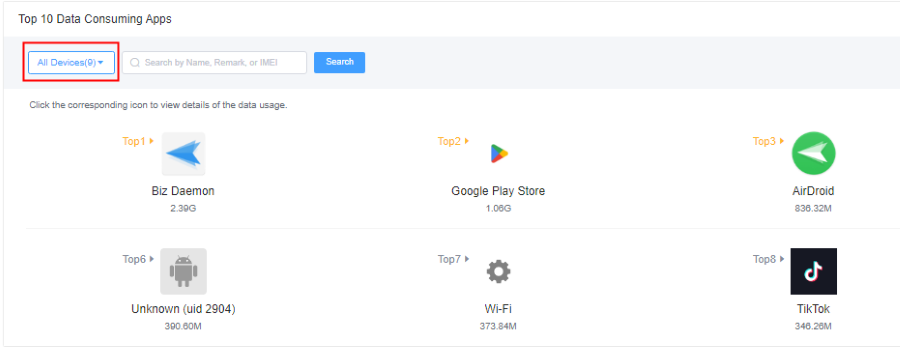
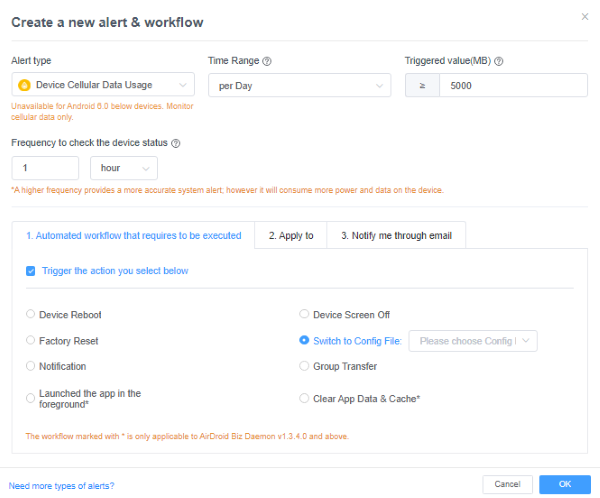
These abilities ensure that IT teams can reduce the frequency of mobile hotspot usage and, in turn, the associated threats.
For example, companies may advise employees to only use mobile hotspots when absolutely necessary for work and avoid its use for non-work functions. The company may even want to provide cybersecurity education on the dangers of mobile hotspot use, so employees are more likely to comply.
If the problem still persists, the company can evaluate whether it needs to escalate from network monitoring to a complete prohibition to best meet its network security needs.
4 A complete prohibition to prevent mobile hotspot security vulnerabilities
Some companies may benefit from a complete prohibition of any mobile hotspot use.
When a prohibition against mobile hotspots may make sense
Some companies operate in susceptible industries. For example, weapons manufacturers have work that involves national security matters, while healthcare companies have a wealth of personal information, such as a patient's medical history.
The trade-off between allowing mobile hotspots for on-the-go work and the associated risks may not be worth it for companies in these industries. In this case, the company may want to prevent using mobile hotspots completely. This step is the only way to ensure complete mitigation of mobile hotspot security vulnerabilities.
How to prohibit mobile hotspots
A company could tell employees that mobile hotspots are banned, but a verbal rule would not be followed. Most employees must remember the restriction; some might even outright disobey the policy. Companies need a guardrail to eliminate the option of using a mobile hotspot altogether.
This elimination can be done via an MDM. After signing up for AirDroid Business, IT teams can create a Policy and Config file that turns off network sharing in the tethering menu.
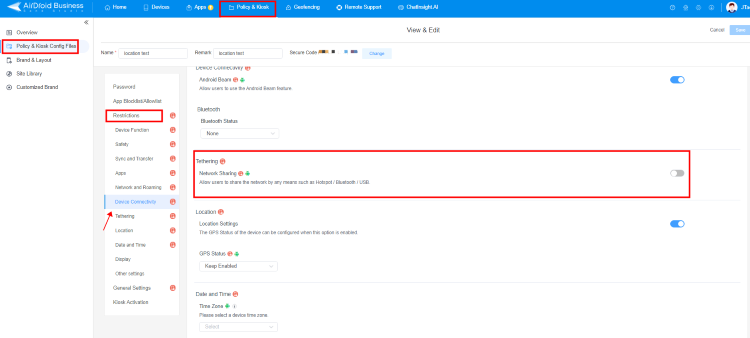
This option prevents using hotspots such as Bluetooth and USB, which are common attack vectors. Upon creating this file, the IT team can select the appropriate devices or groups to apply it to.
Because network monitoring and disabling network sharing are possible through an MDM, enterprises have the ultimate flexibility: They can decide how to deal with mobile hotspot security vulnerabilities in the best way for them.
5 Let your mobile hotspot policy work for you
Mobile hotspots offer great convenience. By tethering their devices to the connection of their phones, employees can work from their laptops or other devices on the go. There is one major problem: Mobile hotspots are not secure.
- Mobile hotspots are vulnerable to a wide range of attacks, including brute force attacks, evil twin attacks, and WiFi jamming, to name a few. Organizations that do not have a strategy around mobile hotspot use thus expose the company to severe risk, which may affect their operations, lead to loss of sensitive data, and damage their brand in the marketplace.
- Organizations thus need an official policy around mobile hotspot use, one aided by an MDM like AirDroid Business. Organizations should take one of two broad approaches. The first is a cautious approach, where IT teams will monitor the network for high data use that may indicate excessive hotspot use. Employees found guilty may be advised to curb their mobile hotspot use only when necessary.
- Alternatively, companies can ban mobile hotspot use together. This prohibition is done by creating a custom Policy and Config file where network sharing is toggled off, which will prevent the use of mobile hotspots and Bluetooth and USB on all relevant devices. Companies that operate in susceptible industries, such as healthcare or financial services, may prefer this restriction.
- With an MDM, organizations can adopt a formal strategy for mobile hotspot use and, more importantly, the most ideal for them. In this way, businesses can enhance network security at scale for all their devices.









Leave a Reply.