Get Answer: What is Zero Touch Provisioning & Process
ZTP, or zero-touch provisioning, is a concept relating to network-connected devices. Today, we will introduce it in this article. What you can expect:
- Zero Touch Provisioning Meaning
- Process Flow of ZTP
- Problems Encountered with ZTP
- ZTP vs OTP vs PnP
- Zero-touch Provisioning in MDM

Part 1: What is Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP)?
Zero-touch provisioning (ZTP) is a deployment method that involves network device auto-configuration.
To better understand the meaning, it's necessary to understand what "touch" specifically refers to. In the context of ZTP, "touch" means manual intervention or interaction. This could be the operations like configuration, setup, installation, and any other physical actions on the device or system. When "zero" is added to it, that is to say, the process requires no human interaction and is replaced with automated processes brought by pre-programmed instructions.
What are Some Practical Uses of Zero Touch Provisioning?
- Network devices - automatic setup for routers, switches, servers, etc.
- Cloud computing - set up and configure virtual machines and containers.
- Internet of Things (IoT) - batch deploy IoT devices.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) - enroll company-owned mobile devices seamlessly.
- Software-defined Networking (SDN) - automatically configure SDN-based firewalls.
Latest Trends in 2023
Zero-touch provisioning is demonstrating consistent market growth as companies work to offer network infrastructure that is in line with commercial demand. The global ZTP market is expected to reach $4.7 billion by 2028, with a growth of 10.1% CAGR. With an ever-growing need to eliminate manual configuration, zero touch provisioning is constantly evolving and the market demand consistently growing.
Additionally, zero-touch provisioning has been applied in mobile device management. Google and Apple, which represent the two major operating systems - Android and iOS, enable ZTP methods for organization-owned devices. And the ZTP applications are called Android Enterprise Zero-Touch Enrollment and Apple Business/School Manager Automated Device Enrollment respectively.
Part 2: How Does Zero Touch Provisioning Work?
Here's a diagram to show how the automated process works.
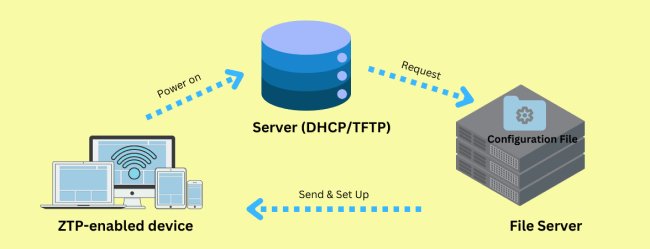
To comprehend the zero touch provisioning process, you will also need to understand several technical terms.
Library for Technical Terms
- Network Device: devices that allow to send, receive, or transmit data using networks, and with.
- Server: cloud-based or on-premise data center for managing access during networking.
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP): network protocol used by devices to request and obtain an IP address and other parameters from a server.
- Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP): file transfer protocol commonly used for automated transfer of configuration or boot files between devices in a local network.
- Configuration File: file with specific settings and parameters for device configuration
- Boot File: file loaded by a device during its startup (or boot) process, which contains instructions that tell the device what to do and how to operate.
- Central Location: in the context of ZTP, this refers to a server or cloud storage service where configuration files are stored and can be accessed by devices.

After you know the meaning of these words, think that you can better understand the diagram. There are three requirements - devices that support ZTP, a server that is able to use DHCP or TFTP, and a file server with configuration files. Now let's go deeper into the process of zero-touch provisioning.
Process of Zero Touch Provisioning (Detailed)
1. A network device that is enabled for Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) arrives at the site and starts up with basic settings.
2. IT teams can make templates for setting up devices. These templates can include network settings, security details, necessary applications, and user choices. This is helpful when setting up many devices at once.
3. The device enters ZTP mode and automatically locates a DHCP server.
4. It automatically reaches out to the server and connects using the IP address, gateway, and DNS server IP address.
5. The device requests a DHCP address.
6. The DHCP server authenticates the device and gives the address for telling it where to find the file server.
7. The device searches for configuration files, running scripts, and software updates in the file server.
8. As the file server provides the configuration profile, the device will install preset configurations.
9. If the device can't find file server information, or if the configuration file has errors, it starts the ZTP process again.
10. The device applies the new settings and ends the ZTP process.
What Comes After the Process of Zero Touch Provisioning?
Once the zero-touch provisioning process is complete, the device is ready to use without any additional configuration or setting up. The company can ship the device to its employee so that he can use it in the workplace. And IT administrators from the organization will carry out follow-ups, such as:
- App updates
- Perform remote troubleshooting
- Device monitoring
- Device management
Part 3: What are Some Typical Problems Encountered with Zero Touch Provisioning?
- Misconfiguration: You may experience errors in the configuration file, particularly if the configuration files are not debugged before they are deployed. ZTP configuration errors can result in set-up errors and security weaknesses.
- Device compatibility: Zero touch provisioning is not compatible with all devices. The network device must have zero touch provisioning capabilities and be able to run more recent software versions.
- Network security: Zero touch provisioning can impact your network security. Remote devices may be less secure compared to other devices, even though they have the same access to the network and any sensitive data. If one device is compromised, the entire zero-touch provisioning network could be compromised.
Part 4: What are the Features of Zero Touch Provisioning?
The main features of zero touch provisioning include:
- Automation: With pre-set configuration files and the Internet, devices are able to deploy efficiently.
- Mass deployment: ZTP allows you to set up company devices on a mass scale. Using a CSV file that includes device model and serial number is available.
- Network required: Zero-touch provisioning requires an established connection between the DHCP or TFTP server and the device.

Part 5: ZTP vs OTP vs PnP: Which is the Best?
When considering what is zero touch provisioning, many people also consider One-Touch Provisioning (OTP) and Plug and Play (PnP). The three terms refer to very similar concepts.
Below is a table summarising the differences between ZTP, OTP, and PnP.
ZTP | OTP | PnP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup | No human intervention; automatically configures when connected to the network. | Need a single manual action to start automatic configuration. | Automatically detects and configures by the operating system. |
| Devices | Network devices like switches, routers, and servers. | Similar with ZTP. | Multiple device types including USB drives, printers, etc. |
| Configuration | Download configuration files from a pre-determined server. | Download configuration files after an action. | Using OS built-in drivers to download |
| Protocols | DHCP and TFTP. | Specific protocols based on the system. | Various protocols depend on the device and OS. |
| Automation Level | Full automation after device connection. | Requires one manual action, then fully automatic. | Automatic detection and configuration by the operating system. |
| Use Case | Large-scale deployments in data centers and enterprise networks. | Scenarios where a single manual initiation is acceptable | For consumer hardware and peripherals, or any scenario where devices need to be used immediately upon connection. |

Part 6: Platforms that Support ZTP
Multiple platforms support zero-touch provisioning, including:
- Cisco - Cisco is a technology company that develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware and software.
- Arista - Arista Networks is a company that provides a variety of software-driven cloud networking solutions for IT environments and large-scale data storage.
- Juniper Networks - Juniper is a company that develops and sells networking products such as routers, switches, software, and security products.
- Cumulus Networks - Cumulus was a computer software company that was absorbed into Nvidia in 2020. They designed and sold a Linux OS for network switches and management software.
Part 7: Zero Touch Provisioning in MDM
Zero-touch provisioning is particularly useful for companies that deploy a large number of mobile devices to their employees, including smartphones, tablet computers, and laptops. It can be used with MDM solutions and here is how they work together:
A company purchases mobile devices that support zero-touch provisioning from a reseller (Android enterprise is recommended). These devices are then registered with the company's zero-touch provisioning enrolment account.
IT administrators then create a configuration file on a zero-touch provisioning console, using the ZTP configuration parameters from MDM solution.
The network devices are shipped to the company’s employees with the MDM- related tools already installed. IT administrators can then manage the devices remotely using zero-touch provisioning and the MDM solution.




Leave a Reply.